How to Choose the Best DisplayPort Cable for Your Needs.

Welcome to our in-depth exploration of DisplayPort! DisplayPort has become the interface of choice for high-quality monitors, catering to gaming enthusiasts who crave immersive graphics and creative professionals who require pinpoint color accuracy. DisplayPort is unique because of its many benefits, including higher bandwidth, enhanced resolution, and support for multi-monitor setups.
When connecting your digital devices, choosing the right DisplayPort cable is crucial. It’s not just about performance, it’s also about the quality of your experience. Whether you’re upgrading your monitor, hooking up your laptop, or setting up your entertainment system, the right cable selection will have a big impact on the end result. In this article, we will provide you with key tips for choosing the ideal DisplayPort cable. And take you to understand the relationship between DisplayPort and USB C port, HDMI and Thunderbolt technology. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, professional, or casual user, we’ll provide you with important information about DisplayPort.
What is DisplayPort Cable?
| / | Transmission Speed | Max. Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| High Bit Rate (HBR) | 10.8 Gbps | 4K/30 Hz |
| High Bit Rate 2 (HBR2) | 17.28 Gbps | 4K @ 60 Hz |
| High Bit Rate 3 (HBR3) | 25.92 Gbps | 4K @ 120 Hz; 8K @ 60 Hz with DSC |
| Ultra High Bitrate (UHBR) | 77.36 Gbps | 8K/60 Hz |
How to Choose a DisplayPort Cable?
In the world of technology, having the right cables is essential for ensuring optimal performance and compatibility. When it comes to displays, one popular option is the DisplayPort cable. But with so many options available, how do you choose the right one? In this section, we will explore the factors to consider when selecting a DisplayPort cable that suits your needs.
Consider the Version:
First and foremost, consider the version of DisplayPort cable you need. DisplayPort cables come in different versions, including DisplayPort 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, and the latest, DisplayPort 1.4. Each version offers its own set of features and capabilities, so it’s important to choose one that is compatible with your equipment.
For example, if you have a 4K monitor that supports DisplayPort 1.2, it is advisable to opt for a DisplayPort 1.2 cable to take full advantage of the display’s capabilities. Conversely, using an older version of the cable may result in limited performance and compatibility. For more detailed basic concepts and version specifications of DisplayPort, you can go to our corresponding blog to learn more.
Consider the Length:
Another important factor to consider when choosing a DisplayPort cable is the length. DisplayPort cables are available in various lengths ranging from a few feet to several meters. It’s crucial to choose a cable that is long enough to connect your devices while taking into account the physical setup of your workspace.
As a general rule of thumb, it’s advisable to opt for the shortest cable length possible to minimize signal degradation. However, if you need to cover a considerable distance, ensure that the cable is of high quality and capable of maintaining signal integrity.
Check the Maximum Resolution and Refresh Rate:
If you’re looking to enjoy high-resolution graphics and smooth video playback, it’s essential to check the maximum resolution and refresh rate supported by the DisplayPort cable. Different cables have different capabilities, so make sure the cable you choose can handle the requirements of your display.
For instance, if you have a 144Hz gaming monitor, ensure that the cable you select can support a refresh rate of 144Hz or higher. Similarly, if you have a 4K monitor, ensure that the cable is capable of transmitting 4K resolution without any loss in quality.
Consider Cable Construction and Quality:
The construction and quality of the DisplayPort cable can also impact its performance and durability. Look for cables that feature gold-plated connectors, as they offer better conductivity and corrosion resistance. These connectors ensure a stable connection and reduce the risk of signal loss.
Additionally, consider the cable’s shielding and thickness. Higher-quality cables often have better shielding, which helps in minimizing electromagnetic interference and signal degradation. Thicker cables are also more robust and less prone to damage. It is always advisable to only invest with a high quality brand to make sure your product comes with a satisfaction and worth the money.
At APPHONE with our high quality products, we guarantee satisfaction and value for your money. Our range of cables boasts superior shielding to minimize interference and signal degradation, while their robust build ensures longevity and protection against damage.
DisplayPort VS USB C Port Parameters.
Mobile devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets are increasingly adopting the USB Type-C™ connector. Although DisplayPort™ and USB Type-C™ technology were initially developed for distinct purposes, the USB Type-C™ interface was designed with a capability to transmit DisplayPort™ signals through an alternate mode.
This feature, known as DisplayPort™ Alt Mode for USB Type-C™, is standardized by VESA. Devices supporting this mode can convey DisplayPort™ signals through the USB Type-C™ port. For instance, a laptop supporting DisplayPort™ Alt Mode can be linked to a DisplayPort™ display using an adapter, such as a USB Type-C™ plug to DisplayPort™ jack.
However, not all devices supporting DisplayPort™ Alt Mode are explicitly labeled. According to the DisplayPort™ organization, most video devices with USB Type-C™ connectors available since 2016 are likely equipped with DisplayPort™ Alt Mode. Products labeled as “Video over USB Type-C™” generally support this feature.
DisplayPort over USB-C merges the USB Type-C port with DisplayPort functionality, facilitating audio/video (AV) transmission. This innovation enables exceptional DisplayPort A/V quality, supporting 4K resolutions and beyond, alongside USB 3.1 data and up to 100W power delivery. DisplayPort was the pioneering A/V protocol adopted via the now widely adopted USB-C connector.
DisplayPort over USB-C typically adheres to the technical specifications of the DisplayPort standard, usually DisplayPort 1.4. Consequently, the USB-C connection allows for transmitting uncompressed 8-bit 4K signals at 120Hz.
DisplayPort VS USB C Port Parameters.
DisplayPort over USB-C, utilizing the DisplayPort 1.4 standard, offers various advantages, including:
- Unrivaled DisplayPort audio and video performance, supporting resolutions up to 8K at 60Hz.
- HDMI 2.0 conversion support for specific products.
- Streamlined usage of USB-C connectors, reducing the need for multiple ports in future devices.
- Up to 4K resolutions at 60Hz with 24-bit color (max 8K at 60Hz).
- 5K compatibility alongside simultaneous USB 2.0.
- Advanced multichannel audio support.
- Compatibility with VESA Display Stream Compression.
- Backward compatible with VGA, DVI, and HDMI 2.0 using plug adapters or adapter cables.
- Employs an extensible packet-based data structure.
- Enables video, SuperSpeed USB, and power all through a single connector.
- Features BT.2020 color space, HDR, and HDCP 2.2 support.
| DisplayPort Port/Cable | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| / | Resolution | Refresh Rate | Chroma/Bits per Pixel (bpp) | Compression | HDR |
| Single Monitor | 1 x 16K (15360×8640) | 60 Hz | 4:4:4/30 bpp | Yes (DSC) | Yes |
| 1 x 10K (10240×4320) | 60 Hz | 4:4:4/24 bpp | No | No | |
| Dual Monitor | 2 x 8K (7680×4320) | 120 Hz | 4:4:4/30 bpp | Yes (DSC) | Yes |
| 2 x 4K (3840×2160) | 144 Hz | 4:4:4/24 bpp | No | No | |
| Triple Monitor | 3 x 10K (10240×4320) | 60 Hz | 4:4:4/30 bpp | Yes (DSC) | Yes |
| 3 x 4K (3840×2160) | 90 Hz | 4:4:4/30 bpp | No | Yes | |
| USB-C Port/Cable (DisplayPort Alt-Mode) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| / | Resolution | Refresh Rate | Chroma/Bits per Pixel (bpp) | Compression | HDR |
| Single Monitor | 1 x 8K (7680×4320) | 30 Hz | 4:4:4/30 bpp | No | Yes |
| Dual Monitor | 2 x 4K (4096×4096) | 120 Hz | 4:4:4/24 bpp | Yes (DSC) | Yes |
| Triple Monitor | 3 x QHD (2560×1440) | 120 Hz | 4:4:4/30 bpp | No | No |
| 3 x 4K (3840×2160) | 144 Hz | 4:4:4/30 bpp | Yes (DSC) | Yes | |
What is the Relationship Between Thunderbolt and DisplayPort?
If you have ever shopped for computer peripherals such as monitors or external storage devices, you might have come across terms like Thunderbolt and DisplayPort. These two terms are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion among consumers. Let’s find out the relationship between Thunderbolt and DisplayPort and clarify their roles and functionality.
Understanding DisplayPort:
DisplayPort is a digital display interface that was developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). It is designed to connect computers or other electronic devices to external displays, such as monitors or projectors. DisplayPort supports high-resolution displays with superior image quality and an array of color options. With the ability to carry audio and video signals, DisplayPort provides a one-stop solution for transmit audio and video, or for transmitting multimedia content from your device to the external display.
Exploring Thunderbolt:
Thunderbolt, on the other hand, is a hardware interface technology developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple. It combines DisplayPort functionality with the high-speed transfer capabilities of PCI Express (PCIe) technology. Thunderbolt offers lightning-fast data transfer speeds, making it suitable for connecting external storage devices, such as hard drives and solid-state drives. Additionally, Thunderbolt supports daisy-chaining, allowing you to connect multiple devices in a series using a single Thunderbolt port.
The Commonality between Thunderbolt and DisplayPort:
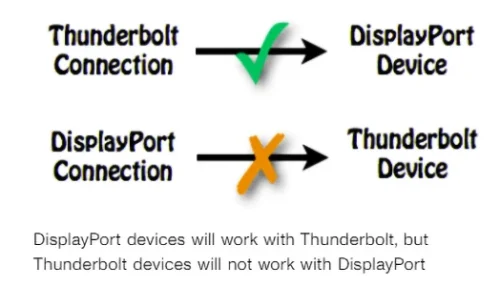
One of the primary reasons for the confusion between Thunderbolt and DisplayPort is their common physical connector. Both Thunderbolt and DisplayPort use the same compact and reversible USB-C connector. This allows devices equipped with Thunderbolt or DisplayPort to be connected to each other using a single cable.
Furthermore, Thunderbolt is fully compatible with DisplayPort. This means that a Thunderbolt port can also support DisplayPort devices, including monitors and projectors. However, it is important to note that not all DisplayPort devices are compatible with Thunderbolt, as Thunderbolt has additional capabilities beyond just display output.
Difference Between DisplayPort and Thunderbolt:
- Video Resolution: DisplayPort 2.0 holds an 8K @ 60Hz resolution, whereas Thunderbolt 4 reaches 4K @ 120 Hz, 4K @ 60 Hz, 5K @ 60Hz, 8K @ 60Hz. Considering that 4K displays are more common with abundant content compared to 8K, be aware of the market availability.
- Multi-Display Connectivity: DisplayPort 2.0 supports two 5K @ 60Hz displays or two 4K @ 144Hz displays and up to six screens at 1080p @ 60Hz. A single Thunderbolt 4 port currently supports one 120Hz 4K monitor + two 60Hz 4K monitors. Alternatively, a single Thunderbolt 4 port can support multiple high-resolution displays simultaneously, including 4K displays with different refresh rates. This can be achieved through the use of a compatible dock or an adapter. It’s also worth noting that Thunderbolt-certified monitors can be directly connected to a Thunderbolt 4 port without the need for additional adapters or docks. And Thunderbolt is about to launch a more advanced Thunderbolt 5, which will support more and higher-definition video connections.
- Data Transmission: DisplayPort 2.0 attains a unidirectional 80 Gbps bandwidth, while Thunderbolt 4 ports offer an impressive bidirectional bandwidth of 40Gbps, allowing for rapid data transfer to and from external storage devices. This high-speed connectivity enables efficient file transfers, ensuring quick and seamless access to your data. Additionally, Thunderbolt 4 ports support the connection of up to five Thunderbolt devices, providing flexibility in device configurations.
- Connector Identification: Distinguishing between mini DisplayPort and Thunderbolt connectors might be challenging due to their similar appearance. DisplayPort ports often have a symbol representing the connector, while Thunderbolt is usually denoted by a lightning symbol.
DisplayPort Vs HDMI: Which Should I Choose?
Both HDMI and DisplayPort are digital systems that replaced older analog systems like VGA, designed to transmit high-definition digital audio and video from a source device to a display. Despite serving the same fundamental purpose, they differ significantly.
While both share certain similarities in image quality, their distinctions are notable. DisplayPort and HDMI cables are intended for different applications, have different connectors, and are not interchangeable.
DisplayPort is commonly used for video transmission on PCs, laptops, and tablets but isn’t extensively employed in consumer electronics, unlike HDMI. One crucial distinction is that producers are not required to pay a subscription fee for DisplayPort, whereas HDMI mandates licensing by the manufacturer.
Furthermore, additional features help distinguish between the two. DisplayPort enables the connection of multiple displays with a single cable, particularly beneficial for professional applications. In contrast, HDMI can only drive a single display per cable. However, HDMI supports an ARC (Audio Return Channel) enabling sound transmission from the display to the source device, a capability not present in DisplayPort.
When to Choose DisplayPort and When to HDMI?
Choosing between DisplayPort and HDMI largely depends on the specific use case and device compatibility:
- Home Theater Setups: For home theater systems, HDMI is often preferred as many TVs lack a DisplayPort input, making HDMI more compatible with consumer electronics.
- Gaming:For gaming consoles with HDMI 2.0 or higher as the only output, HDMI is the primary choice. However, for PC gaming, DisplayPort is generally superior if your computer supports it, offering higher refresh rates and compatibility with advanced gaming features.
- Laptop to TV/Projector Connections: When connecting a laptop to a TV or projector, HDMI is a reliable option as it is widely supported by most devices.
- Multiple Monitor Setups:DisplayPort is preferable for connecting a laptop to multiple monitors. While HDMI usually supports a single screen, DisplayPort allows daisy-chaining or utilizing multi-stream transport (MST) to connect multiple monitors.
- Adapter Usage:Adapters can bridge the connection between devices with only HDMI or DisplayPort outputs to ensure compatibility.
Considering these factors will help make an informed decision tailored to your specific needs and device compatibility. Whether you opt for DisplayPort or HDMI, each offers unique advantages. Choosing the right cable ensures optimal performance and an enhanced display experience.
I believe that through the above introduction of APPHONE, you already have a certain understanding of different audio & video communication technologies. It’s time to choose the right connection cable for your device. If you need high-quality DisplayPort cables, whether you need mass production or customized production, we have the ability to provide you with a solution.
We specialize in providing customers with high-performance connectivity solutions, no matter how specific your needs are, we offer custom production, personalized solutions specifically designed to meet your business needs. When you work with us, you’ll receive high-quality products and excellent customer service. Don’t hesitate to contact us, APPHONE looks forward to providing you with the best connection solutions.
Who owns and develops DisplayPort Standards?
The Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) is responsible for owning and developing the DisplayPort standards.
What is the current version of the DisplayPort Standard?
The current version of the DisplayPort standard is Display port 2.0, with version 2.1 being the most recent iteration.
What are the important features of DisplayPort 2.0 and 2.1?
Display Port 2.0 and 2.1 boast enhanced features, including support for high resolutions such as 8K and beyond, increased refresh rates, HDR support, and higher bandwidth for faster data transfer.
Which types of products include DisplayPort?
DisplayPort is commonly found in PCs, laptops, tablets, monitors, docking stations, and various professional AV equipment.
How is DisplayPort different from HDMI? Aren’t they very similar?
DisplayPort and HDMI share the purpose of transmitting high-definition digital audio and video but are different in their applications, display port connector connectors, and subscription requirements for manufacturers.
How has the adoption of Thunderbolt affected DisplayPort?
Thunderbolt technology utilizes the DisplayPort protocol, thereby integrating DisplayPort features and capabilities. Thunderbolt’s adoption has expanded the reach of DisplayPort technology.

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up