Guide to measuring and selecting the appropriate USB cable gauge.

In the previous article, we have talked about what is wire gauge? And its impact and common specifications in USB cables. But many customers still want to know how to measure and verify the wire gauge model, and how to choose the appropriate wire gauge based on the economic effect when purchasing. I worked with the APPHONE engineering team to sort out the hot topics among customers and answer their questions here.
How To Measure Wire Gauge?
When working with electrical wiring, understanding how to measure wire gauge is essential for ensuring the correct wire is used for specific applications, ensuring it can safely handle the electrical load. Additionally, utilising custom wire winding and bending techniques can optimise your electrical projects. Below are the straightforward steps to accurately measure your wire gauge.
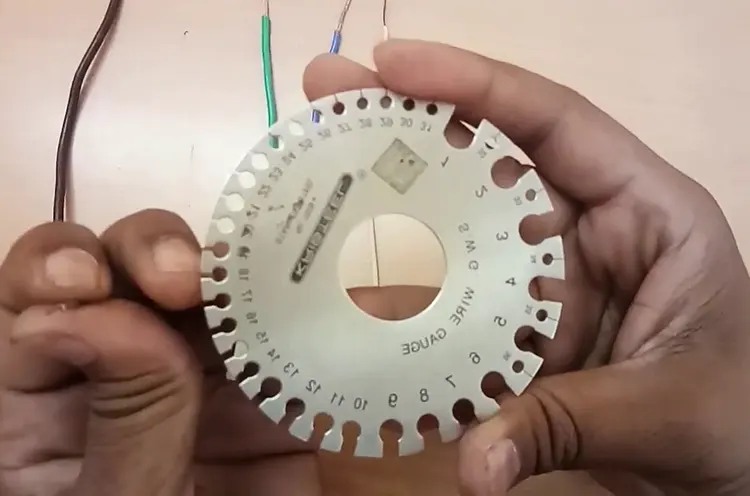
Step 1: Gather Your Tools
Before you begin measuring, make sure you have all the necessary tools ready. You’ll need a wire gauge measurement tool, often called a wire gauge or wire gauge metre, which can be found at local hardware stores or online. Ensure that you have a striped wire free of insulation for measurement. Note that wire gauge tools come in two types: standard (American Wire Gauge, AWG) and metric (measured in millimetres), so choose one that aligns with your gauge system.
Step 2: Measure the Wire Diameter
Position your stripped wire between the jaws of the gauge tool and gently close them around the wire. The tool should grip the wire securely without exerting excessive pressure. Look for the number indicated on the tool that corresponds to the wire diameter.
Step 3: Identify the Wire Gauge
With the diameter measured, refer to a wire gauge chart to identify the corresponding wire gauge. These charts are readily available online and outline wire gauge sizes alongside their diameters. Locate the diameter you noted in Step 2 and find the matching wire gauge size.
Step 4: Verify Your Measurements
For accuracy, it’s wise to double-check your results. Repeat the measuring process from Steps 2 and 3 to confirm the wire gauge.
Step 5: Select the Correct Wire Gauge
Once you’ve determined the wire gauge, select the appropriate wire for your project or repair. Using the wrong gauge can lead to circuit overload or malfunction. Refer to a wire gauge chart to ensure you choose the correct wire for your specific needs. Additionally, custom wire winding and bending services can provide wires tailored to your specifications, including gauge size, length, and insulation type.
Step 6: Validate with a Micrometre
If you wish to ensure the precision of your measurement, use a micrometre to measure the wire’s diameter. This tool provides an accurate measurement for small diameters. If the micrometre reading aligns with your initial wire gauge measurement, you can trust the results.
If you do not have access to a wire gauge tool or micrometre, numerous online resources or wire gauge calculators can help you determine the wire gauge. For instance, in the above table we provided detailed wire gauges and their corresponding measurements. While these online tools can be helpful, they may not be as precise as using a physical gauge or micrometre, so keep that in mind.
How To Choose The Right Wire Gauge For Your Usb Cable?
Choosing the appropriate wire gauge for your USB cable is a critical step in ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and safety. USB cables serve various purposes, from charging devices to high-speed data transfer, so selecting the right gauge is essential for meeting your specific needs. Here’s a detailed guide on the key factors to consider when determining the right wire gauge for your USB cable.
Current Requirements
Understanding the current (measured in amperes) that your device requires is the first step in choosing the correct wire gauge. Devices with higher power demands, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, require thicker wires with lower gauge numbers. This is because thicker wires can carry more current without overheating. It should be noted that USB cables usually consist of four wires (high-performance and high-power USB cables will require 5 wires): two for power and two for data, while the power wires range from 20 to 28 AWG. This configuration ensures efficient power delivery while maintaining reliable data transfer, making it essential to choose the right wire gauge based on your device’s specific requirements.
Cable Length
The length of your USB cable plays a significant role in determining the appropriate wire gauge. Longer cables experience increased resistance, which can lead to voltage drop and affect the performance of the cable. For cables longer than 2 metres (about 6.5 feet), it is wise to select a thicker gauge to compensate for the resistance and ensure efficient power delivery and data transfer. For example, if you’re using a cable longer than 3 metres, consider using an 20 AWG wire or thicker.
Data Transfer Needs
If your USB cable is intended for high-speed data transfer, such as for USB 3.0 or higher standards, the gauge of the wire becomes even more critical. Thicker wires help maintain signal integrity by reducing the amount of electromagnetic interference that can disrupt data transmission. For high-speed applications, a wire gauge of 28 AWG or thicker is often recommended to ensure reliable data transfer rates without significant loss or degradation.
Voltage Drop
Minimising voltage drop is essential, especially for cables over 2 metres. Voltage drop can reduce the amount of power reaching your device, resulting in slower charging times or, in some cases, preventing the device from charging altogether. To mitigate voltage drop, choose a thicker wire gauge, such as 20 AWG or lower, for longer cables. This will help ensure that sufficient voltage reaches your device, optimising charging efficiency and performance.
Flexibility and Durability
Flexibility is an important consideration, especially if your USB cable will be frequently bent or twisted. Thinner wires tend to be more flexible, making them easier to handle in tight spaces. However, they may not provide the durability needed for constant bending and flexing. If you need a cable that can withstand regular movement, balance flexibility with durability by opting for a wire gauge that meets your needs without sacrificing longevity. For example, a 22 AWG wire sizes might provide a good compromise between flexibility and durability for most everyday applications.
Application Type
Consider the primary application of your USB cable. Will it be used mainly for charging, data transfer, or both? Charging-focused cables benefit from thicker wires to handle higher currents, while data cables may prioritise wire quality to ensure signal integrity. If the cable will serve both functions, err on the side of caution and select a thicker gauge to ensure reliable performance in all scenarios.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select the right wire gauge for your USB cable. At APPHONE, we prioritize quality and reliability, using first-class wires to ensure optimal performance. We adhere to strict composite wire gauge standards, tailoring our production to meet customer-specified data transmission and fast charging requirements. This thoughtful approach guarantees that your cable is not only efficient but also capable of meeting the demands of your devices. Remember, investing in the correct wire gauge can prevent potential issues down the line and enhance the overall user experience with your electronics.
How many amps can 10 gauge wire handle?
A 10 gauge wire can typically handle up to 30 amps for short runs and around 25 amps for longer distances. This variation is due to the increased resistance that occurs in longer wire runs, which can cause the wire to heat up more significantly. It’s essential to consider the length of the wire run when determining the appropriate gauge.
How many amps can 14 gauge wire handle?
A 14 gauge wire can handle up to 15 amps safely. This makes it suitable for lighting circuits and standard household outlets. However, it’s important to note that if the wire is used in a situation where it is bundled with other wires or in an area where heat cannot dissipate, it may be necessary to de-rate its ampacity to avoid overheating.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up








