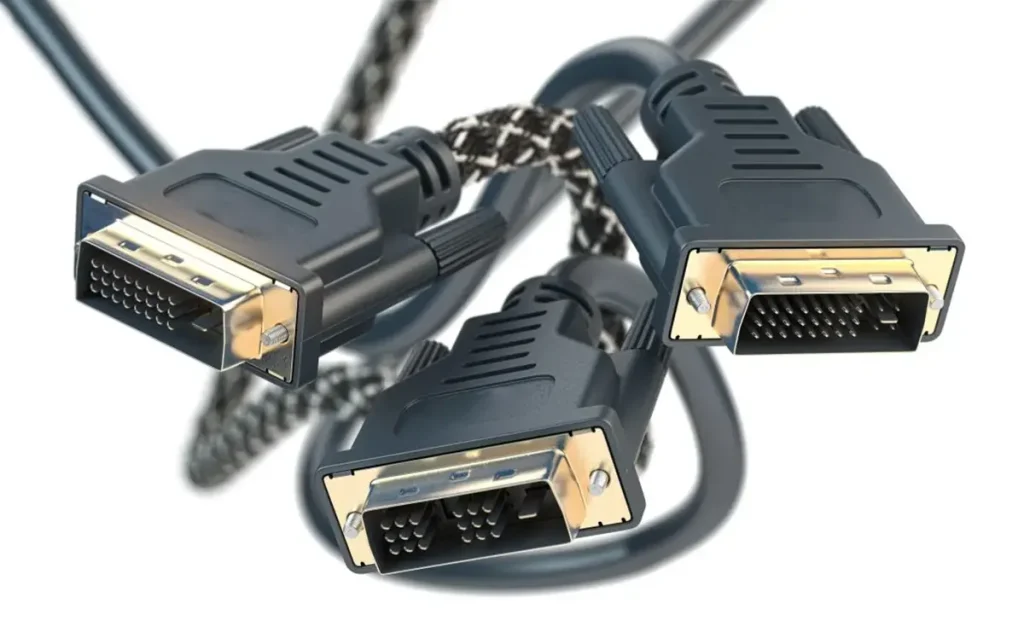
Guide to DVI Cable Types, Compatibility, and How They Work

In today’s digital age, connectivity and visual clarity are paramount, especially in industries reliant on cutting-edge display technology. Enter the Digital Visual Interface (DVI) – a revolutionary solution designed to elevate connectivity and visual fidelity to unprecedented levels. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of DVI cables, exploring their functionality, compatibility, and significance in modern computing and display environments. Join us as we unravel the wonders of DVI technology and its transformative impact on digital display setups.
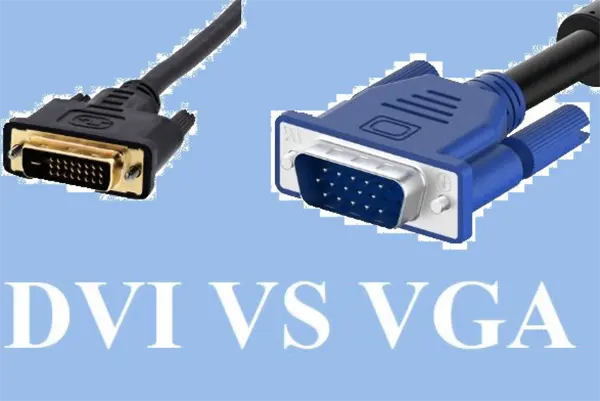
What is a DVI cable?
DVI, short for Digital Visual Interface, provides significantly clearer and superior images compared to VGA. It functions as a unique connector capable of transmitting both digital and analog signals and is easily adaptable to other standards like HDMI and VGA.
Developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG), DVI serves as a digital visual interface supporting both digital and analog video signals through a single cable. Widely utilized in computers, LCD monitors, projectors, and other digital display devices, DVI cable has become a popular video interface technology aimed at enhancing the quality of flat-panel LCD monitors and modern video graphics cards.
Replacing the short-lived P&D Plug & Display standard and advancing beyond the pure digital DFP format of old flat-panel displays, DVI cables are favored by video card manufacturers, with most featuring one or two DVI output ports.
In addition to its role as a standard computer interface, DVI cable has been a preferred digital transmission method for HDTVs and other high-end video displays used in television, movies, and DVDs. Some high-end DVD players even include DVI outputs alongside high-quality analog component video. While the digital market has shifted towards HDMI interfaces for high-definition media transmission, DVI cable remains specialized for the computer market.
How Does a DVI Cable Work?
The working principle of DVI (Digital Visual Interface) cable revolves around the transmission of digital signals, facilitating the transfer of high-quality video data from source devices like computers or DVD players to display devices such as monitors, televisions, or projectors. DVI cables are preferred for their ability to deliver pristine video transmission, devoid of the distortion and interference commonly associated with analog signals, thereby making them indispensable for applications demanding high-resolution image displays and graphics-intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, and design work.
DVI cables are available in various types, each tailored to specific needs: DVI-D (digital only), DVI-A (analog only), and DVI-I (digital and analog integrated). Selecting the appropriate type hinges on the compatibility between the source and display devices. Although some LCD monitors possess the capability to accept analog signals and internally convert them to digital format, the dominance of digital operation underscores the widespread adoption of the DVI format.
The core of the DVI cable specification lies in Silicon Image’s Transmission Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS) technology. This innovation facilitates a high-speed digital interface by transmitting digital information through a transmitter on the video adapter to the receiver on the display. TMDS technology not only retrieves the signal from the video adapter but also discerns the monitor’s resolution and refresh rate, thereby optimizing signal distribution over the available bandwidth to ensure seamless data transfer from the computer to the monitor.
Expanding upon the working principle of DVI cables, it’s crucial to delve into their compatibility with various devices and the benefits they offer in terms of ease of installation, stability, and adaptability to evolving display technologies. DVI cables provide users with a plug-and-play solution, eliminating the need for complex setup procedures. Their stability and reliability ensure consistent signal integrity over extended distances, making them suitable for professional environments where image quality is paramount.
Moreover, the adaptability of DVI cables to different resolutions and refresh rates allows users to tailor their display settings according to their preferences and hardware capabilities. With support for multiple resolutions and refresh rates, DVI cables offer scalability to accommodate future display technologies and hardware upgrades, ensuring long-term compatibility and performance.
What Are the Different Types of DVI Cables?
DVI (Digital Visual Interface) cable is a key connection device for digital video signal transmission. It is usually used to connect computers, DVD players or other digital devices to display devices such as monitors, TVs or projectors. DVI cables provide a variety of connection options to meet the needs of digital video signal transmission between different devices.
- DVI to HDMI cable:
DVI to HDMI cable is used to connect a device with a DVI output port to a display device with an HDMI input port. This connectivity option allows users to transmit digital video signals from a computer, game console, or other device to the HDMI port of a TV or monitor and enjoy high-definition images and audio. - DVI to DisplayPort cable:
A DVI to DisplayPort cable is used to connect a device with a DVI output port to a display device with a DisplayPort input port. Through this connection, users can transmit video signals from computers or other digital devices to monitors that support the DisplayPort interface to achieve high-quality video display. - DVI to VGA cable:
DVI to VGA cable is used to connect a device with a DVI output port to an older monitor or projector with a VGA input port. Although VGA has been gradually replaced by HDMI and DisplayPort, there are still many older devices using the VGA interface. Through DVI to VGA cables, users can transmit video signals from digital devices to these old-fashioned display devices to achieve compatibility connections.
Overall, DVI cables offer a variety of connection options, allowing users to choose the most suitable connection method based on their device and monitor’s interface. Whether connected to HDMI, DisplayPort or VGA interface, DVI cable can provide high-quality and reliable digital video signal transmission, bringing users a high-quality visual experience.
Are all DVI cables compatible?
DVI (Digital Visual Interface) connectors come in three main types: DVI-A (analog), DVI-D (digital), and DVI-I (integrated; analog and digital). Each type of connector has unique functions and uses.
– The DVI-A connector is used to transmit analog video signals and is suitable for connecting devices that support analog signals such as old CRT monitors or projectors. The DVI-A connector is compatible with DVI-A and DVI-I cables as it supports analog signal transmission.
– The DVI-D connector is designed to transmit digital video signals and can be connected to digital display devices such as LCD monitors or digital TVs. The DVI-D connector is only compatible with DVI-D and DVI-I cables because it does not carry analog signals.
– DVI-I connector combines analog and digital signal transmission functions and is suitable for various types of display devices and source devices. The DVI-I connector is fully compatible with DVI-D, which means any LCD monitor with a DVI-D connector will work well with the DVI-I socket on your computer’s graphics card.
What is the difference between DVI and VGA cables?
The main distinction between DVI and VGA cables lies in their signal types, image quality, and hardware compatibility. Both connectors are utilized to transmit video from a source, such as a computer, to a display device, such as a monitor, TV, or projector. In the realm of display connectivity, understanding the disparities between DVI and VGA cables is essential for optimizing visual output. These two stalwarts of video transmission possess distinct characteristics, ranging from signal type to resolution support, influencing their suitability for various devices and applications.
- Signal Type and Quality:
VGA connectors and cables are capable of transmitting analog signals exclusively, making them suitable for older display devices or systems that still utilize analog technology. In contrast, DVI cables have the versatility to transmit both analog and digital signals, offering a significant advantage in terms of image clarity and quality, particularly when connecting to modern high-resolution displays.
DVI cables generally provide better signal quality, especially for higher resolutions, due to their ability to transmit pure digital signals without conversion. This dual capability of DVI makes it a more advanced option compared to VGA. - Connector Types:
DVI connectors come in three main types: DVI-I (integrated analog and digital), DVI-D (digital only), and DVI-A (analog only). This versatility allows for compatibility with different devices and signal types.
VGA connectors are standardized with a D-subminiature (D-sub or DE-15) connector, typically featuring 15 pins arranged in three rows. They can be either male or female, with protruding pins or socket receptacles, respectively. - Resolution Support:
Furthermore, DVI connectors typically provide superior image quality compared to VGA due to their ability to transmit digital signals. DVI cables support higher resolutions and faster data transmission rates compared to VGA cables. This makes DVI more suitable for modern displays with higher pixel densities and refresh rates.
VGA cables are limited in resolution support, typically maxing out at 640×480 (VGA) or 800×600 (SVGA), making them less ideal for high-definition displays. - Compatibility and Applications:
DVI cables are commonly used in newer display devices such as LCD monitors, digital projectors, and HDTVs due to their superior signal quality and resolution support.
VGA cables are still prevalent in older or legacy devices, as well as in industrial settings where reliability and durability are prioritized over high-resolution output. - Length and Interference:
DVI cables can maintain signal integrity over longer distances compared to VGA cables, especially when using shielded or higher-quality cables.
VGA cables may experience more signal degradation and interference, particularly over extended lengths, due to their analog nature and susceptibility to electrical interference.
In summary, while both DVI and VGA cables serve the purpose of connecting display devices to video sources, DVI offers superior signal quality, resolution support, and versatility, especially for modern high-definition displays. VGA, while still widely used in certain applications, is gradually being phased out in favor of digital interfaces like DVI and HDMI.
What is the difference between DVI and HDMI cables?
Amidst the array of cables and connectors, the choice between HDMI and DVI stands out as a fundamental decision. Each bears its own unique characteristics, impacting not just the physical setup but also the quality of our digital experiences. Let’s delve into the intricacies of HDMI and DVI, unraveling their distinctions to empower informed decisions in crafting our digital workspaces.
- Physical Footprint:
DVI: Typically features a larger, rectangular plug with securing screws on the sides.
HDMI: Adopts a more compact design with a slim rectangular plug and no securing screws, making it more space-efficient. - Compatibility:
DVI: Commonly found in older hardware configurations, such as desktop computers and some monitors.
HDMI: More prevalent in modern devices like laptops, TVs, gaming consoles, and multimedia devices due to its smaller connector size and wider adoption. - Quality and Performance:
DVI: Limited in terms of maximum resolution and refresh rates, with a maximum data rate of 9.9 Gbit/sec.
HDMI: Supports higher resolutions and refresh rates, with the latest HDMI 2.1 standard capable of handling resolutions up to 8K at 120 Hz and a maximum data rate of 42.6 Gbit/sec. - Audio Support:
DVI: Does not support audio transmission, requiring separate audio cables for sound output.
HDMI: Capable of transmitting both digital video and audio signals over the same cable, eliminating the need for additional audio connections. - Price and Availability:
DVI: Generally le6. Recommendation:
ss common and may be slightly more expensive due to its older technology.
HDMI: More widely available and often cheaper due to its widespread adoption and compatibility with modern devices.
As we wrap up our comparison between HDMI and DVI, it’s clear that these connectors play a significant role in shaping our digital experiences. Whether it’s the sleek design of HDMI or the robust capabilities of DVI, each offers a unique solution for connecting our devices seamlessly. In the realm of creativity, where efficiency is key, grasping these differences empowers us to tailor our setups to our needs. - Recommendation:
DVI: Suitable for legacy devices with DVI ports or specific hardware requirements where HDMI is not available.
HDMI: Preferred for modern setups due to its superior performance, broader compatibility, and convenience of transmitting both video and audio signals.
As we wrap up our comparison between HDMI and DVI, it’s clear that these connectors play a significant role in shaping our digital experiences. Whether it’s the sleek design of HDMI or the robust capabilities of DVI, each offers a unique solution for connecting our devices seamlessly. In the realm of creativity, where efficiency is key, grasping these differences empowers us to tailor our setups to our needs.
What should I do if my DVI connection does not work properly?
When encountering the ‘no signal’ issue on your DVI-connected monitor in a dual monitor setup, you can try the following steps to resolve it:
- Check DVI cable and connections: Firstly, ensure that the DVI cable is securely connected to both the monitor and the graphics card on your computer, and check if the cable is in good condition. Loose connections can sometimes cause signal problems. Try unplugging and re-plugging the DVI cable to ensure a snug fit.
- Update graphics drivers: Outdated or incompatible graphics drivers often lead to display issues. Make sure you have the latest drivers installed for your graphics card. You can usually find the latest drivers on the manufacturer’s website.
- Boot in safe mode: Since you mentioned that the DVI-connected monitor works in safe mode, there may be a driver conflict causing the issue. Try booting into safe mode and uninstall any graphics drivers. Then, restart your computer and let Windows reinstall the drivers automatically.
- Check BIOS settings: Sometimes BIOS settings may interfere with dual monitor setups. Enter your computer’s BIOS (usually by pressing the Delete or F2 key during boot-up) and check if there are any settings related to multiple displays. Try resetting the BIOS settings to their defaults.
- Swap DVI ports: If your graphics card has multiple DVI ports, try connecting the DVI cable to a different port and see if the issue persists. This can help identify if there’s a problem with a specific port.
- Test with different DVI cable: If none of the above solutions work, consider trying a different DVI cable, or if you’re using any DVI adapters (e.g., DVI to HDMI or DVI to DisplayPort), try using different ones. Faulty cables or adapters can sometimes cause signal issues.
- Check resolution and refresh rate: Ensure that the resolution and refresh rate settings for the DVI-connected monitor are within its supported range. You can try setting them to the same values as the VGA-connected monitor and see if that helps establish the connection.
If you’re still experiencing issues after trying these steps, consider reaching out to technical support for further assistance. By following these troubleshooting steps, you can hopefully resolve the ‘no signal’ issue on your DVI-connected monitor and ensure smooth operation of your dual monitor setup.
Why is DVI important to computer users?
DVI is important for computer users because it provides a high-quality digital video signal that can be transmitted over longer distances than analog signals like VGA. This makes it ideal for use with large displays or multiple monitors, where image quality and clarity are critical. Additionally, many modern graphics cards and displays only support digital connections like DVI or HDMI, so having a DVI connection allows you to take full advantage of these features.
In conclusion, the versatility and performance of DVI cables make them indispensable in modern digital display setups. At APPHONE, we understand the importance of tailored connectivity solutions to meet diverse needs. With our expertise in DVI cable customization, we offer support for various connector ports, dual-link configurations, sheath types, lengths, and port shapes, ensuring seamless integration and optimal performance for every application. Whether you require standard lengths or bespoke solutions, we’re committed to providing high-quality DVI cables tailored to your specifications through batch customization and OEM services. Partner with us for your DVI cable needs and experience unmatched reliability and performance in your digital display setups.
What is the maximum specified length for a DVI cable?
Up to five meters. DVI cables will function at their best signal quality. Given that DVI-I (integrated) can handle both digital and analog signals, the 5-meter limit also applies to it.
Are DVI to HDMI cables directional?
A computer can be connected to a TV or monitor using an HDMI to DVI cable; these cables support DVI to HDMI and can be used in either direction.
Can i connect two monitors with a DVI cable?
Sure! You can easily connect two monitors with DVI ports to a computer equipped with either two DVI ports or a mix of DVI and HDMI ports. This can be achieved using either a graphics card designed for dual-monitor setups or by utilizing a combination of the computer’s built-in graphics ports and an additional graphics card.
What is the difference between DVI and VGA cables?
The main difference between A: DVI and VGA cables is signal type, picture quality and hardware compatibility. VGA cable transmits analog signals, while DVI cables can transmit numbers and simulation signals. Because DVI is a newer technology, it provides a clearer video output than VGA; however, VGA can support longer cable lengths. DVI cable was launched by the digital display working group in 1999. By providing digital and simulation signal transmission capabilities, the display technology was completely changed. This versatility makes the video output clearer when the real color palette is displayed on the computer display. In contrast, the VGA cable was first pioneered by IBM in 1987, and specially transmitted analog signal. Although the VGA cable is older, it is still very common. 99%of the desktop computer monitors are equipped with a VGA interface, and more than 70%of tablet TVs support the VGA connection with the projector.
What is the difference between DVI and VGA cables?
DVI (DIGITAL VISUAL Interface) is an abbreviation of digital visual interface. It is a unique connector that can transmit digital and simulation signals, and can easily adapt to other standards such as HDMI and VGA. As a digital video interface, DVI supports digital and analog video signals through a single cable. Widely used in digital display devices such as computers, LCD displays, projectors, etc., DVI has become a popular video interface technology, which aims to improve the quality of tablet LCD displays and modern video graphics cards.
What should I do if my DVI connection is not working properly?
If you are having problems with your DVI connection, there are a few things you can try. First, check that all cables are securely connected at both ends and look for signs of damage or wear. Next, try restarting your computer or display to see if that resolves the issue. Finally, you may need to update your graphics card driver or adjust some settings in your computer’s Display Settings menu to ensure your images are scaled and aligned correctly.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up