Understanding DVI Technology: Types, Differences, and Connectivity Essentials

In an era where digital connectivity reigns supreme, understanding the intricacies of DVI (Digital Visual Interface) technology is paramount. As technology evolves, so do our connectivity options, and DVI remains a stalwart in delivering high-quality video signals to our displays.
Our guide aims to unravel the mysteries of DVI technology, from its inception to its various types and connectivity essentials. Whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or a newcomer to the world of digital interfaces, this comprehensive exploration will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the digital landscape with confidence.
Join us as we embark on a journey through the realm of DVI, uncovering its nuances, deciphering its types, and delving into its connectivity essentials.
What is digital visual interface?
The Digital Visual Interface (DVI) serves as a crucial link between display devices, like LCD monitors or projectors, and output devices, transmitting video signals, whether analog or digital. Unlike other interfaces like VGA and HDMI, which handle both video and audio signals, DVI focuses solely on delivering high-quality video signals to your monitor.
Renowned for its ability to enhance visual quality, DVI is commonly associated with devices like LCD monitors, projectors, and TVs, providing users with clear and crisp images for an optimal viewing experience.
Developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG), DVI emerged as a solution to replace outdated analog-based video display systems, facilitating the transmission of uncompressed data to specific display devices. The standard supports both analog and digital signals, making it versatile for various display setups and enabling a seamless transition from analog to digital displays. At its core, the DVI standard utilizes transition-minimised differential signaling (TMDS), optimizing data transmission by minimizing the number of transitions required. This balanced approach enhances the data-transfer rate and accuracy, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of DVI connections.
What are the types of digital visual interfaces?
DVI-A (analog), DVI-D (digital), and DVI-I (integrated; analog and digital) are the three varieties of DVI connectors. Single link and dual link are the two distinct data rates available for DVI-I and DVI-D interfaces. To prevent data corruption during the transfer of data from the video card to the monitor, there is a maximum data rate allowed for each type of link.
Let’s delve deeper into the realm of Digital Visual Interface (DVI) connectors and explore the intricacies of their various types. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for optimizing connectivity in your digital setup.
DVI-A – High-Res Analog
The DVI-A connector has 17 pins (12+5), lacks a dual-link option, and only carries analog signals, similar to VGA signals but with a different configuration. Click to learn what exactly a VGA cable is. To connect a VGA video card to a DVI-A monitor, or vice versa, a VGA to DVI adapter is required. Since VGA is primarily used in analog monitors and DVI is the standard for digital signals, the DVI-A connector is relatively uncommon compared to the DVI-I and DVI-D connectors. DVI-A cables are compatible with DVI-A and DVI-I connectors, but DVI-D cables cannot be used with DVI-A connectors because they do not carry any analog signals. DVI-A is an older version of DVI, which stands for Digital Visual Interface-Analog, and can only transmit analog signals, not digital signals from the monitor, with a maximum resolution of 1920*1080. The DVI-A connector features a cross in the upper right corner with 2 pins on top and 2 pins on the bottom, as well as an additional 12 pins.
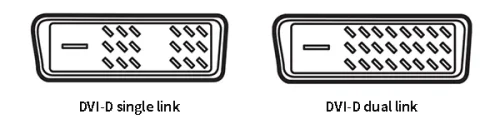
DVI-D – True Digital Video
DVI-D connectors are specifically designed to transmit digital video signals and come in two variants: single-chain and dual-chain. A single-link DVI-D connector has 19 pins (18+1), while a dual-link connector has 25 pins (24+1).
DVI-D cable is compatible with DVI-D and DVI-I connectors. However, it’s important to note that DVI-D does not support additional features such as integrated audio and CEC control, which are found in HDMI and DisplayPort connections. While HDMI and DisplayPort connectors can support DVI-D video signals through adapters, the reverse is not true. DVI-D connectors are typically found on most digital monitors, while those that support both digital and analog signals typically have DVI-D and VGA connectors. It’s worth mentioning that DVI-A and DVI-I cables cannot be used with DVI-D connectors due to the lack of extra analog pins.
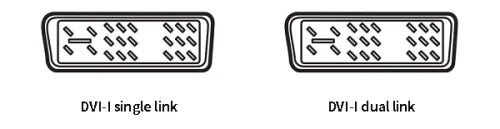
DVI-I – The Best of Both Worlds
The DVI-I connector, available in single-link and dual-link variants, features 23 pins (18+5) for single-link and 29 pins (24+5) for dual-link configurations. DVI-I connectors do not convert between analog and digital signals but can accept either one—though not simultaneously. When both digital and analog signals are available from the video card, monitor, and cable, a selection must be made.
Despite its versatility, DVI-I connectors are compatible with all three types of DVI cables. However, due to the extra analog pins, male DVI-I cables are not suitable for female DVI-D connectors. Consequently, DVI-D cables are the most commonly used among the three cable types, considering the rarity of DVI-A connectors. DVI-I cables can transmit either analog or digital video signals and are compatible with both DVI-A and DVI-D connections. They also come in single-link and dual-link versions, with the single-link supporting a maximum resolution of 1600 * 1200 and the dual-link supporting a maximum resolution of 2048 * 1536.
What is a Dual Link DVI Cable?
A dual-link DVI cable is an advanced version of the standard DVI cable, designed to support higher resolutions and faster refresh rates. Unlike single-link DVI cables, which have fewer pins and are limited in their data transmission capacity, dual-link DVI cables feature additional pins and pathways, allowing for increased bandwidth and enhanced performance.
Dual-link DVI cables can support resolutions up to 2048 x 1536 at 60 Hz. Each link in a dual-link DVI cable has three data channels for RGB information, with a maximum bandwidth of 165 MHz, equivalent to 1.65 billion pixels per second. These cables utilize all 24 pins for transmission, providing the necessary bandwidth to deliver high-resolution images with clarity and detail.
In addition to these technical specifications, dual-link DVI cables offer several advantages:
- Higher Bandwidth: Dual-link DVI cables have twice the bandwidth of single-link DVI cables, allowing for the transmission of larger amounts of data. This results in higher resolutions and faster refresh rates.
- Support for High-Resolution Displays: Dual-link DVI cables can support high-resolution displays, including 1440p (WQHD), 1600p, and even 4K resolutions. This makes them ideal for connecting to high-end monitors and displays requiring greater pixel density and clarity.
- Refresh Rate Support: Dual-link DVI cables enable faster refresh rates compared to single-link cables, crucial for smooth motion and reduced screen tearing in gaming and multimedia applications.
- Professional Applications: Commonly used in professional environments like graphic design studios and medical imaging facilities, dual-link DVI cables offer high-resolution support and color accuracy, essential for precise image rendering and reproduction.
- Compatibility: While offering advanced performance, dual-link DVI cables remain backward compatible with single-link DVI ports, allowing flexibility in connectivity.
- Digital Signal Transmission: Like single-link DVI cables, dual-link DVI cables transmit digital signals, ensuring high-quality image reproduction without analog signal interference, resulting in sharper images and accurate color representation.
- Longer Cable Lengths: Dual-link DVI cables typically support longer cable lengths, providing flexibility in cable routing and setup configurations, especially in larger workspaces or multimedia installations.
- Application in Gaming: Popular among gamers, dual-link DVI cables deliver high-resolution, high-refresh-rate gaming experiences, contributing to smoother gameplay and enhanced visual fidelity.
HOW to connect a DVI cable?
In order to get a clearer and more exciting visual experience, you have purchased a new high-definition monitor and are ready to connect it to your computer. Below are the steps to connect the DVI cable.
- Preparation: Make sure your computer and monitor are turned off and have the DVI cable ready.
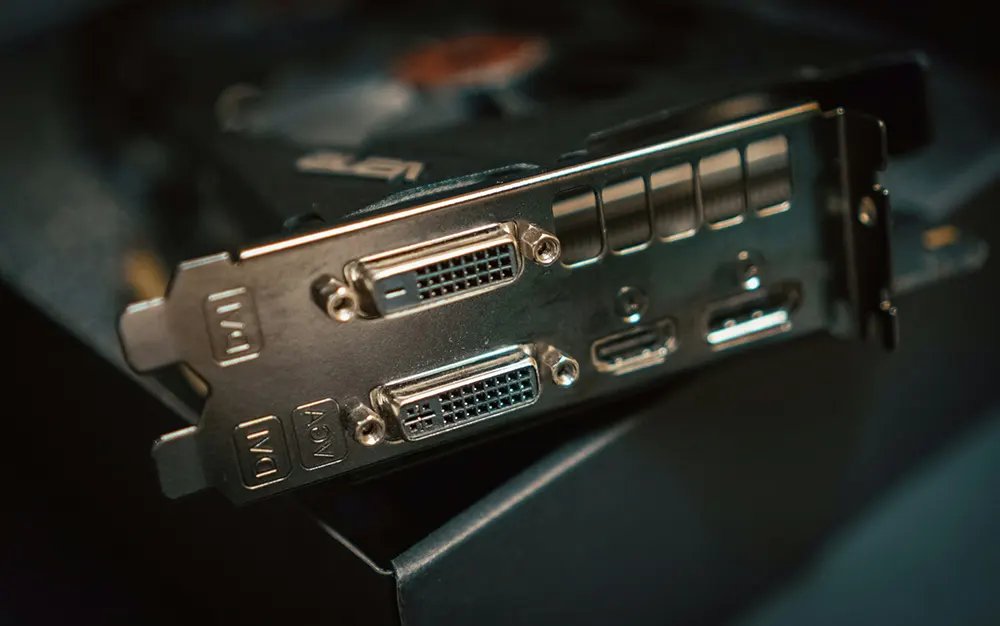
- Locate the port: Locate the output port labeled “DVI” on the back panel of your computer or graphics card. There will usually be an arrangement of small pinholes.
- Plug in the cable: Take one end of the DVI cable and connect it to your computer’s DVI output port. Make sure the cable’s connector is aligned with the port and insert it gently but firmly until you hear a slight “click” indicating a secure connection.
- Connect the monitor: Find the DVI input port on the back of the monitor, usually it is located together with other input ports (such as HDMI, VGA). Plug the other end of the cable into the monitor’s DVI input port, again making sure it’s aligned and plugged into place.
- Turn on your device: Now, turn on your computer and monitor. The monitor may display “No Signal” or other similar message, this is normal.
- Select the input source: Use the buttons on the monitor or the remote control to switch the input source to DVI. In the monitor’s menu, select “Input” or “Source” and then select DVI as the input source.
- Adjust settings (if necessary): In your computer’s operating system, open the Display settings menu. Adjust resolution, refresh rate, and other display options as needed to ensure optimal image quality.
After completing the above steps, your computer and monitor should be successfully connected, and you can start enjoying a clearer and more exciting visual experience.
What is the difference between DVI and DisplayPort cables?
To understand the differences between DVI (Digital Visual Interface) and DisplayPort, it’s essential to delve into their respective technologies and capabilities. Below, we explore various aspects that distinguish these two interfaces, shedding light on their strengths and applications.
The main differences between DVI (Digital Visual Interface) and DisplayPort are as follows:
- Technology: DVI was designed to replace VGA and was commonly used in the early 2000s, while DisplayPort is a more recent technology that offers higher resolutions, color depths, and refresh rates compared to DVI.
- Resolution and Color Depth: DisplayPort supports higher resolutions, color depths, and faster refresh speeds than DVI. This makes it particularly suitable for professional applications such as photography, video editing, scientific research, engineering, and CAD design.
- Compatibility: While both DVI and DisplayPort have their own versions and standards, DisplayPort cables generally offer more features and capabilities compared to DVI cables. DisplayPort monitors often support 10-bit color depth, which is beneficial for tasks that require accurate color representation.
- Use Cases: DisplayPort is favored by professional users such as photographers, video editors, engineers, and CAD designers due to its higher capabilities and support for advanced features like 10-bit color depth. However, for general users and older systems, DVI may still be sufficient, especially if the monitor only has VGA and DVI ports available.
- Data transfer speed: DisplayPort generally offers higher data transfer speeds, which means it is able to support higher resolutions and refresh rates. According to some professional reviews, DisplayPort versions 1.4 and 1.4a even support 8K resolution displays.
- Number of connections and multi-streaming: DisplayPort also supports multi-streaming, which means one interface can connect multiple monitors at the same time, while DVI requires multiple interfaces to connect multiple monitors.
- Audio support: Unlike DVI, DisplayPort is not only able to transmit video signals, but also audio signals. This means that HD video and audio signals can be transmitted simultaneously through a single DisplayPort connection without the need for additional audio cables.
- Monitor technology support: DisplayPort technology is also more compatible with emerging monitor technologies, such as Adaptive Sync and High Dynamic Range (HDR), which can provide a smoother gaming experience and better visual effects.
- Future development: As DisplayPort technology continues to develop and update, it is likely to become the mainstream connection standard for future monitors and graphics processors, replacing the current DVI and HDMI interfaces.
In short, while DVI has been a standard interface for many years and still serves its purpose in certain scenarios, DisplayPort offers significant advantages in terms of resolution, color depth, compatibility, and future-proofing. Its support for higher resolutions, faster refresh rates, multi-streaming, audio transmission, and compatibility with emerging monitor technologies makes it the preferred choice for professionals and enthusiasts alike. As technology continues to evolve, DisplayPort has already established itself as the mainstream connection standard for modern monitors and graphics processors, having surpassed the limitations of older interfaces like DVI. With its ability to support higher resolutions, faster refresh rates, and advanced features, DisplayPort remains at the forefront of digital display connectivity, ensuring compatibility with the latest devices and technologies.
What type of DVI cable do i need?
When selecting DVI connection cables, it is crucial to consider compatibility and signal requirements. Once device compatibility is determined, choosing the appropriate cable becomes simpler. DVI cables offer various options tailored to different signal types.
- For digital signals, it is advisable to use pure DVI-D cables. If both devices utilize DVI connections, a standard DVI-D cable will suffice. However, if one end is HDMI, a DVI-D to HDMI cable is necessary.
- For analog connections, especially over shorter distances, integrated adapter cables prove convenient. These cables feature DVI plugs on one end and either VGA or 5-BNC plugs on the other. Alternatively, if VGA cables are used, a compact DVI/VGA adapter paired with existing cables can serve the purpose.
- For longer distances, it is recommended to utilize a full-size RGBHV cable setup. One end is equipped with male BNC terminations, while the other includes a male DVI plug and a five-female BNC breakout adapter. Using full-size cables helps minimize signal loss, particularly over extended distances, by maintaining impedance and minimizing signal quality loss compared to miniature cables.
Understanding the various DVI cable options and their intended applications empowers users to make informed decisions based on specific connectivity needs.
For instance, if connecting a computer to a display monitor, a standard DVI-D cable may be chosen. If linking a computer to a projector or television, a DVI-D to HDMI cable might be necessary. For video projection in conference rooms, school classrooms, or large event venues, employing a full-size RGBHV cable setup ensures stable signal transmission.
Additionally, considering factors such as appropriate cable length and quality standards is essential. Ensuring the selected cable’s length adequately covers the required distance and possesses sufficient quality to guarantee signal stability and connection reliability is paramount.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues with DVI Connections.
In the journey through DVI technology, challenges often arise, from signal disruptions to resolution issues. To assist, this guide offers practical solutions to common DVI connection problems. Let’s explore and troubleshoot together for a seamless viewing experience.
- No Signal or Black Screen:
Check Connections: Ensure that the DVI cable is securely plugged into the correct ports on both the computer and the monitor. Loose or incorrectly inserted connections can result in a lack of signal or a black screen.
Replace Cable: If possible, try using a different DVI cable to rule out any cable-related issues.
Adjust Monitor Input Source: Verify that the monitor is set to the correct input source. Sometimes, monitors may default to the wrong input source, causing no signal or black screen issues. - Incorrect Display Resolution:
Adjust Display Settings: Open the display settings menu in your computer’s operating system and adjust the resolution settings to match the optimal resolution of your monitor. Selecting a resolution that matches your monitor’s specifications can improve image quality and clarity.
Update Graphics Card Drivers: Sometimes, the correct resolution for your monitor may depend on the support provided by your computer’s graphics card drivers. Try updating your graphics card drivers to the latest version and then readjust the resolution settings. - Color Abnormalities:
Check Connections: Color abnormalities may be caused by poor contact or damage to the DVI cable. Ensure that the DVI cable is properly connected and free of breaks or damage.
Adjust Display Settings: Open the display settings menu in your computer’s operating system and try adjusting the color calibration options. Sometimes, tweaking the display settings can resolve color abnormalities. - Monitor Not Recognized:
Reconnect: Try unplugging and reconnecting the DVI cable. Sometimes, reseating the connection can resolve issues with unrecognized monitors.
Update Graphics Card Drivers: Ensure that your computer’s graphics card drivers are correctly installed and up to date. Issues with unrecognized monitors may sometimes be due to problems with graphics card drivers.
As technology advances and connectivity needs diversify, the demand for tailored DVI solutions continues to grow. At APPHONE, we specialize in providing customized DVI cables to meet the unique requirements of our customers. Whether it’s matching different connector ports, configuring dual-link setups, selecting specific cable lengths, or shaping connectors to fit unique form factors, we support a wide range of customization options. With our commitment to quality, precision, and customer satisfaction, we empower you to enhance your connectivity solutions with confidence. Contact us today to explore our comprehensive DVI cable customization services and experience seamless connectivity tailored to your specific needs.
Can i use DVI D cable on DVI I port?
DVI-I seamlessly integrates with DVI-D, ensuring compatibility between flat panel monitors equipped with DVI-D connectors and video cards featuring DVI-I receptacles. Since January 2002, Dell flat panel monitors have been outfitted with DVI-D ports, facilitating smooth operation with both DVI-D and DVI-I video connectors.
Do DVI cables carry audio?
DVI exclusively handles video signals and does not have the capability to transmit audio. Consequently, because the DVI port on the connected device lacks audio output, the HDMI connection on the TV remains devoid of any audio input. As a result, while the DVI-to-HDMI cable delivers the visual content to the TV screen, the TV speakers remain unable to produce any sound.
Does my display support DVI connection?
To determine whether your display supports DVI connection, you can view the specification table or manual of the display. Generally, the display supporting DVI connection will list the DVI connection information in the connection interface part. You can also check the back or side of the display to see if there are DVI interfaces. If you are not sure, you can also contact the display manufacturer or refer to online support resources to obtain help.
Does my computer support DVI output?
To determine whether your computer supports DVI output, you can view the graphical output port of the computer. If your computer has a DVI output port, it usually indicates the word “DVI” around the port. You can also check the computer specification table or manual to understand the video output options they support. If you are not sure, you can consult or check online support resources to obtain more information with computer manufacturers.
Can I change between DVI and HDMI?
Yes, you can use the adapter to convert the DVI signal to the HDMI signal, and vice versa. This means that if your computer has a DVI output port and the display has HDMI input port, you can use DVI to HDMI adapter to connect the two. Similarly, if your device has an HDMI output port and the display has a DVI input port, you can use HDMI to DVI adapter to achieve connection. These adapters can usually be purchased in electronic equipment stores or online markets.
Share This Artcle:

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up