USB Power Delivery: Effect, Safety performance and its versions.
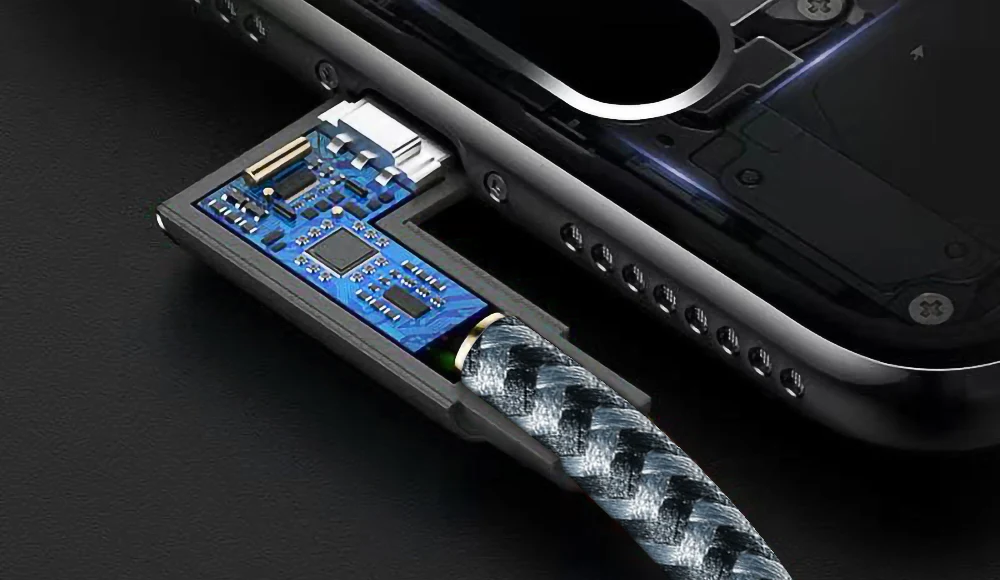

Our lives are increasingly inseparable from various smart devices, which have changed our lives, entertainment and work. But any electronic device requires power support, and in recent years a fast charging technology is making charging simple and fast – USB-Power Delivery (USB PD).
What is USB PD?
USB-Power Delivery (PD) protocol is a fast charging technology based on the USB-C standard, which is like the superhero of fast charging. It’s been around since 2012, coinciding with the debut of the USB-C port. Before USB PD charging protocol, we were stuck with slower USB battery charging standards. But then, USB-PD swooped in, created by USB-IF, and answered the call from laptop manufacturers for a connector that could deliver more power. It aimed to maximize the available power sent to devices.
When people talk about “fast charging” technology, they’re often talking about USB Power Delivery. USB-PD allows devices to communicate with each other before transferring power, so they can negotiate and deliver just the right amount needed. It’s all about efficient, intelligent power delivery – no more, no less! So, when you’re in need of a quick charge, USB-PD is the tech that’s got your back.
The latest USB-PD 3.1 standard can deliver a whopping 240 watts of power. That’s a significant leap from the previous maximum of 100 watts. However, it’s important to note that not every scenario will deliver the full 240 watts. The actual power delivery depends on the cable and the device’s maximum wattage support. If your device doesn’t support it, you won’t be feeding it a whopping 240 watts; it’s more likely to be too much for it to handle! This is why some cables use E-Marker chips to detect a device’s wattage needs and adjust the power flow accordingly.
Why is USB Power Delivery important?
USB PD is not just another technology acronym; it is a technology specification. It’s a game changer and is changing the way we charge our devices. USB-C PD can supply a greater amount of power than standard wall chargers, so it is especially useful for getting power back into devices fast. Here are the reasons why the USB-PD charging protocol is so important:
Versatility:
USB-PD is the key to universal fast charging. It works on a variety of devices, from smartphones and laptops to tablets and even accessories like headphones and smartwatches. To avoid the waste of using dedicated chargers for different devices and brands, power delivery USB C simplifies it all.
Higher charging speeds:
USB PD can provide higher levels of power, ranging from 5 watts (W) to 240 watts (W). This is a significant improvement over the limited power transfer of a standard USB connection. This means you can charge your device quickly, whether you’re in a hurry to get out or just don’t want to wait for the battery to recharge.
Dynamic voltage and current:
USB PD is smart and can dynamically adjust voltage and current to meet the specific power requirements of the device. This flexibility allows it to charge a variety of devices and also prevents damage from overloading the device.
Bi-directional charging:
USB PD supports bi-directional charging, which means it can not only provide power to the device, but also receive power from the device. This feature is especially useful for powering laptops or other devices with USB-C ports from an external power source.
Compatibility:
USB PD is compatible with the USB Type-C connector, can be used reversibly, and can carry both power and data. You don’t have to worry about whether your charger matches your device. It uses a common data language that all modern devices understand. Your USB c with power delivery charger can smoothly charge laptops, smartphones and other electronic devices.
Safety features:
Qualcomm QC 4.0 and subsequent versions of charging technology integrated with USB PD include safety features such as overvoltage protection, overcurrent protection and temperature monitoring to ensure safe charging.
Future-proof:
As technology evolves, USB-PD remains future-proof. It continues to adapt to support higher power levels and changing equipment requirements. This means your USB-PD charger is an investment that will serve you well for years to come.
Overall, the USB power delivery specification is a versatile and powerful charging standard that is becoming increasingly popular in the tech industry due to its ability to charge a variety of devices quickly and efficiently. It provides a more universal and standardized approach to fast charging across a variety of devices and manufacturers.
What versions (specifications) of USB PD charging protocol are there?
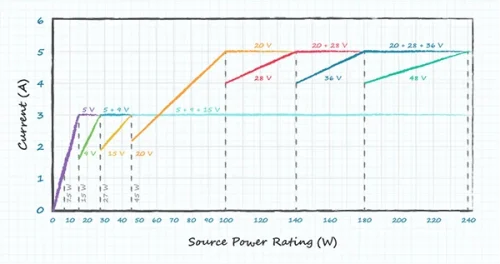
The USB Power Delivery standard has gone through 4 iterations, with each new version introducing improvements and expanded functionality. The voltage has been upgraded from 5V, 9V, 12V, 15V and 20V to 28V, 36V and 48V. Power output range is 0.5W to 240W. The following are the specification parameters of each version of the USB PD charging protocol:
| USB PD Protocol Versions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USB PD Specification | Rated voltage/V | Current range/A | Power range/W | Application equipment |
| USB PD 1.0 | 5 | 2 | 10 | Headphones and other small accessories; |
| 12 | 1.5 | 18 | Mobile phone, iPad, etc. | |
| 12 | 3 | 36 | Mobile phones, notebooks and adapters, etc. | |
| 20 | 3 | 60 | Hubs, routers, etc. | |
| USB PD 2.0/3.0 | 5 | 0.1-3.0 | 0.5-15 | Headphones, hard drives and other small accessories |
| 9 | 1.67-3.0 | 15-27 | Mobile phones, cameras, drones, etc. | |
| 15 | 1.8-3.0 | 27-45 | iPad, smartphone, etc. | |
| 20 | 2.25-3.0; 3.0-5.0(Requires specific cable support); | 45-100 | Monitors, laptops, etc. | |
| 28 | 3.57-5.0 | 140 | Monitors, laptops, etc. | |
| 36 | 3.89-5.0 | 180 | ||
| 48 | 3.75-5.0 | 240 | ||
Although the USB PD protocol has detailed specifications, the actual voltage, current and power transfer depends on the capabilities of the charger and the device being charged. USB PD will automatically identify the parameters at both ends to determine the best power transmission to ensure safe and efficient charging.
Is USB Power Delivery safe?
Yes, you can use USB Power Delivery technology with confidence as it provides an efficient and safe way to charge your electronic devices.
Nowadays, USB PD chargers are highly intelligent, and one of the key factors is the E-Marker chip built into the fast charging cable. The main job of this tiny chip is to detect and identify your connected device and provide it with the power it needs to ensure fast and safe charging. This means your device will be charged at the optimal speed without having to worry about excessive current damaging the circuit. Click to learn how fast charging cables change your life.
Although USB PD charging is safe in most cases, some users may have concerns about its safety. This is mainly because some low-quality USB PD cables or chargers may remove the E-Marker chip to reduce costs. In this case, there may be some safety hazards of USB PD fast charging.
At APPHONE, we strongly recommend that when customers choose USB PD cables and chargers, especially when charging power requirements are high, they must choose products equipped with E-Marker chips to ensure charging efficiency and safety. In this way, you can enjoy the convenience of fast charging, and at the same time, you can use it with confidence without worrying about the problems that may be caused by poor quality products.
Is USB C equal to USB PD?
USB C (also known as USB Type-C) and USB PD are related but different technologies in the world of USB connectivity. Anyone who knows a little bit knows that chargers with USB-PD protocol output via USB C, but this cannot simply be used to determine whether it is a charger that supports USB-PD protocol. A charger with Type-C output does not necessarily support the USB-PD protocol; a charger that supports the USB-PD protocol must have a Type-C output. These two terms are not interchangeable. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between them:
- Functionality: USB-C mainly refers to the physical connector itself, while USB-PD is a specific power transfer protocol that can be implemented through the USB-C connector. In other words, USB-C is the port side of USB connectors (Click to learn more about connector types), while USB-PD focuses on how power protocols are transmitted and managed.
- Power Delivery:At the heart of USB-PD is adaptive power delivery, enabling higher power levels and dynamic power management. USB-C itself does not provide information about power transmission capabilities, but the number of pins it provides can be adapted to different USB protocols as needed.
- Compatibility: USB-C is widely used as a connector for a variety of devices, including smartphones, laptops, tablets, and accessories. However, not all USB-C ports support USB-PD Power Delivery. Some devices may use USB-C for data transfer and other functions, but lack USB-PD support for fast charging.
- Standards:USB-PD has different versions and standards (e.g., USB-PD 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 3.1) that define the functionality and power levels it can provide. As a connector, USB-C currently uses a unified appearance standard, but it can adapt to USB 2.0-4.0 transmission standards.

To sum up, USB-C and USB-PD are complementary technologies. The key difference between USB Type-C and USB-PD is that USB Type-C is a reversible USB connector that has a small form factor, while USB-PD is a power delivery protocol that allows for up to 240W power delivery. Confusion often arises among users because many devices that use USB-C connectors also support USB-PD fast charging. Users might think that USB-C automatically means fast charging, but that’s not always the case. USB-C is only a physical connector; actual charging speed depends on the device’s USB-PD implementation. So it is essential to check the device specifications and charger compatibility for the best charging experience.
What are the limitations of USB power delivery?
Through the above explanation, I believe everyone has a certain understanding of the capabilities and characteristics of USB Power Delivery. So what are the shortcomings (or what are the limiting factors) of the promotion of PD fast charging technology? Let’s take a look:
- Complexity:USB-PD’s adaptability and multiple power profiles can make it complex to implement. It requires careful management of voltage, current, and power delivery, which can be challenging for manufacturers.
- Device Support: Not all devices and chargers support USB-PD, leading to compatibility issues. Users need to ensure that both the charger and the device are USB-PD compatible to benefit from fast charging.
- Cable Quality: To support high-power delivery, USB-PD cables need to be of high quality and meet specific standards. Using low-quality cables can result in slower charging or even damage to devices.
- Cost:USB-PD chargers and cables can be more expensive than traditional chargers and cables due to their enhanced capabilities and quality requirements.
- Power Source: To fully leverage USB-PD’s fast charging capabilities, you need a power source (charger) that supports USB-PD. Older chargers may not provide the desired charging speed.
- Device Awareness: USB-PD relies on devices and chargers communicating their capabilities and requirements. If a device or charger doesn’t negotiate properly, it may not deliver the expected fast charging speed.
You’ve learned about the capabilities of USB Power Delivery and how it can provide a faster, more efficient charging experience for your devices. Now, it’s time to bring this powerful technology into your business.
As a professional custom USB cable manufacturer, we are proficient in USB-PD technology and lead the industry with customized production capabilities. Whether you need USB-PD charging cables with specific specifications, or other USB-related products, we can provide you with high-quality, customized solutions.
Stop worrying about mismatched chargers or inefficient charging. Work with us to make your product charging experience faster and more convenient. Contact us now to initiate an inquiry, and we will provide you with customized USB-PD solutions to meet your needs!

Fast delivery
Fastest delivery within 22 days

Quick proofing
Fastest 3-day proofing cycle

After-sale protection
24-month long warranty

1V1Customer Service
Professional customer service follow-up